| |
 |
| |
 |
| (1) The Reason Why the Numerical Analysis is necessary. |
| (2) Difference Method and Finite Element Method |
| (2)-1 Difference Method |
| (2)-2 Finite Element Method |
| (3) Important Items for Finite Element Method |
| (3)-1 Dividing Elements and Calculation Conditions |
| (3)-2 Formula for Elements |
| (4) Validation of the Results of the Finite Element Method |
| |
| |
 |
| (1) The Reason Why the Numerical Analysis is necessary. |
| |
| The differential equations, such as the thermal conductivity equitation, describes the phenomena. Therefore, if we can solve the differential equations, we can get the equations for the phenomena. |
| |
| The solutions of the differential equations are the analytical ones. The analytical solutions contains no error. Therefore, it is very precise and useful. However, unfortunately, the analytical solutions are very rare to obtain. The famous analytical solution of the thermal conductivity equitation is a kind of an exception. It is for a thin line and the temperature of both ends are zero (0) degrees. |
| |
| The numerical solutions do contain errors. But the most importantly, we can obtain the solutions. As long as the errors are small enough for our purposes, the numerical solutions are very useful. It is well know how to minimize the error. In my humble opinion, both of the difference method and the finite element one are the champions of the numerical analysis. |
| |
| The reason why we need the numerical analysis it to solve the differential equations, which no analytical ones are obtained. |
| |
 |
| (2)-1 Difference Method |
| |
| I may be wrong, but please let me summarize the difference method and the finite element method as following. |
| |
| The difference method directly replaces the differential formula with the difference ones. |
| |
| To be more specific, the differential equations can be expressed as an infinite sum of series. The difference method is to use the finite numbers of the infinite series, say the first three (3) series, and the rest of the infinite series is expresses as an error. |
| |
| The error is portional to the difference size. Therefore, if we take the size is small enough, the error becomes small enough as well. |
| |
| Please see the "Simulation", "Difference Method" for detail. |
| |
| (2)-2 Finite Element Method |
| |
| The finite element method is to divide the material into finite elements, and indirect system equations are introduced in the elements. |
| |
| Therefore, the numbers and the types of the elements and the validity of the system equations do determine the outcome. The analyst who decides the elements and creates the system of equations must examine the results. |
| |
| The following texts shows the important items for the use of the finite element method. |
| |
 |
| (3) Important Items for Finite Element Method |
| |
| As said above, both of the elements and the system of equations within elements are very important. Therefore, the adequate knowledge for the material and for the process are necessary. The more knowledge and in many cases the more experience, the better and the simpler system of equations. |
| |
| Many programs are commercially available, and it may not be necessary for you to make a program by yourselves; however, the deeper knowledge, the more efficient for the use of those commercial ones. |
| |
 |
| (3)-1 Dividing Elements and Calculation Conditions |
| |
| When you apply the finite element method for the structual analysis, the important items are the size and the type of the elements. Another important one is how to apply the external force to the elements. How many elements should share the "concentrated" load? Does it act on a vertex or on a side? These conditions, which you decide, do affect the outcome. |
| |
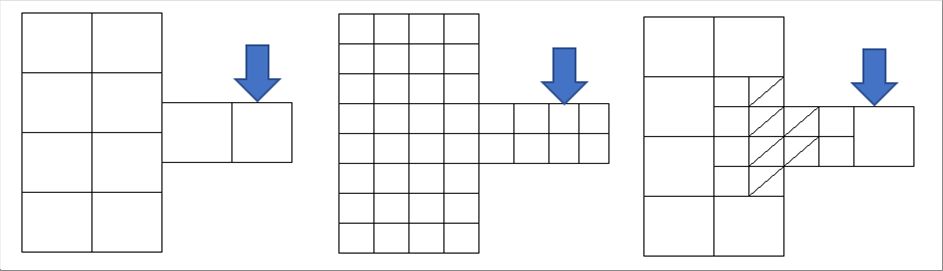 |
| |
| The above three (3) pictures show the examples of the elements and the load condition to a same material. We see big elements in the left one, smaller elements in the middle, and the combination of triangle, small squares, and big squares in the right. |
| |
| The concentrated load is applied on the top side of the element. There are two (2) sizes in the pictures, big or small. If we choose a better cell, the small one may be adequate. |
| |
| Furthermore, the actual "concentrated" load is shared by small area of the material. Therefore, it may be necessary to divide the cell into two (2) or more smaller elements in order to reflect the reality. |
| |
| When we apply the finite element method to the metal plastic deformation analysis, the material should be divided into adequate elements according to the knowledge of the metal plastic deformation theory. |
| |
| One of the difference between the structural analysis and the metal plastic deformation one is the load. The load for the metal plastic deformation is sometimes not the calculation condition, but the outcome. And another is the deformation of material. It is the outcome of the structural analysis, but it is the calculation condition for the metal plastic deformation analysis. |
| |
| The following three (3) pictures show the dividing elements of the roll and the material during the hot rolling. It is necessary to adopt the adequate elements for the analysis purpose. |
| |
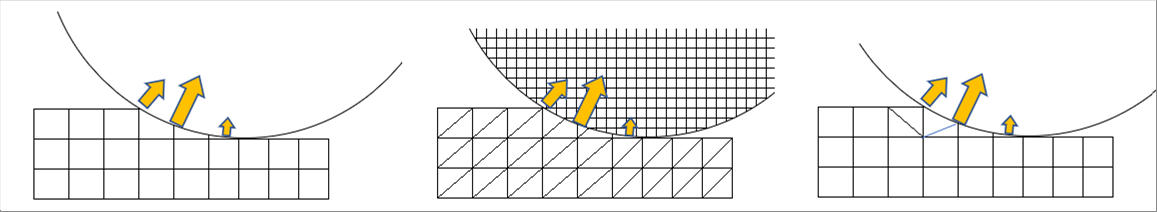 |
| |
 |
| (3)-2 Formula for Elements |
| |
| There is no rule for the formula, which are applied to the elements. Therefore, there are wide range of applications. However, the specialized knowledge is necessary. |
| |
| The linear equations are good as the formula for the elements, because the linear algebra formulas are utilized. Please note that it is necessary to define the formula for the elements based on the most adequate knowledge for the analysis among the material dynamics, the thermodynamics, the fluid dynamics, the metal plastic deformation theory, and so on. |
| |
| For example, the elastic deformation is linear, but once the deformation reaches the elastic limit, it becomes non-linear. The thermal conductivity equations and the equations of motion of fluids (the Navier-Stokes equations) are also non-linear. |
| |
| One example of the non-linear equations for the elements is the energy. It is considered that the energy is kept minimum for the whole process of the deformation. Intuitively, it sounds true. When we need a cup of boiled water, we always need the same quantity of gas, for example. If the change happens due to more than the minimum one, the quantity of gas always vary. Same to the metal deformation. |
| |
| The following picture indicates the deformation energy and the friction loss one of a hot plate rolling. We can express the deformation energy by the strain, which we can calculate from the deformation velocity. The friction loss can be obtained by the combination of the pressure and the friction coefficient. And then, the total energy of whole area can be minimized. It is necessary to solve the partial differential equations in order to obtain the minimum value. If the partial differential equations are expressed in a system of first-order equations or in a system of quadratic equations, the rest of the calculation become easy. |
| |
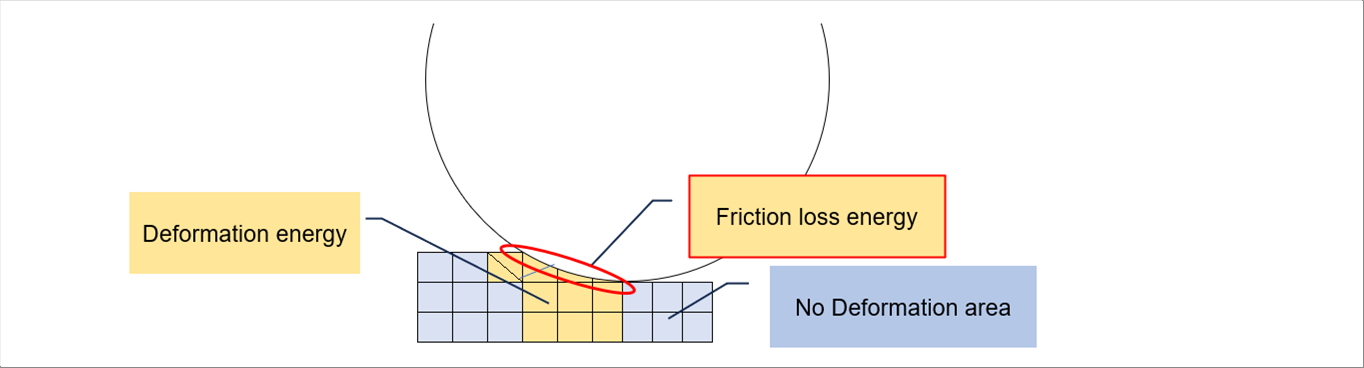 |
| |
| If we use the finite element method for the temperature analysis, the thermal conductivity equations are applicable. However, as said before, no analytical solution is obtained. Instead, if we have the temperature estimation formula for the material, the calculation becomes easy. The experimental formula may be adequate for the temperature estimation formula. Apparently, the accuracy of the temperature estimation formula do affect the outcome. |
| |
| Same as the hot rolling, if the formula in elements are expressed in either systems of first or second-order equations, the rest of the calculation becomes convenient. |
| |
 |
| (4) Validation of the Results of the Finite Element Method |
| |
| As we have been thinking, the numeric solutions of the finite element methods are dully affected by the knowledge of the analyst. The important items are the elements, the systems of equations in the elements, how to apply the loads, boundary conditions of the temperature, and so on. |
| |
| Therefore, it is absolutely necessary for the analyst to determine the validity of the results. |
| |
| The best way of the validation may be to compare the experimental results or the comparison against the actual process. Another suggestion for the analyst to grasp the results as quick as possible is to utilize the visualization of the calculated results. Colors for different ranges of the values, or the three dimensional (3D) distribution graphics are suggested. |
| |
| Author: T. Oda |
| The page was prepared in Excel, and automatic html and css generation by the "excel2web". |
| |





















